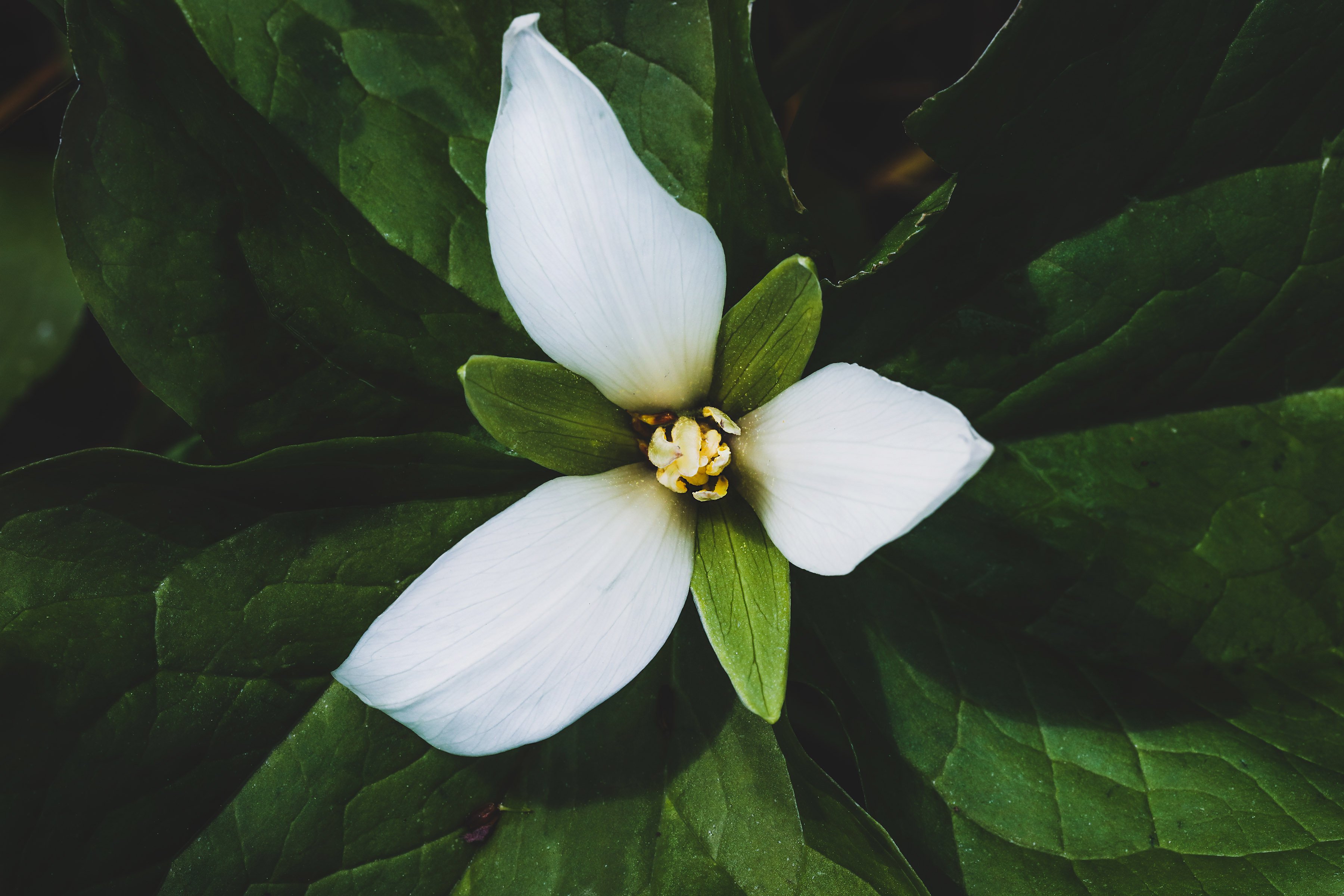
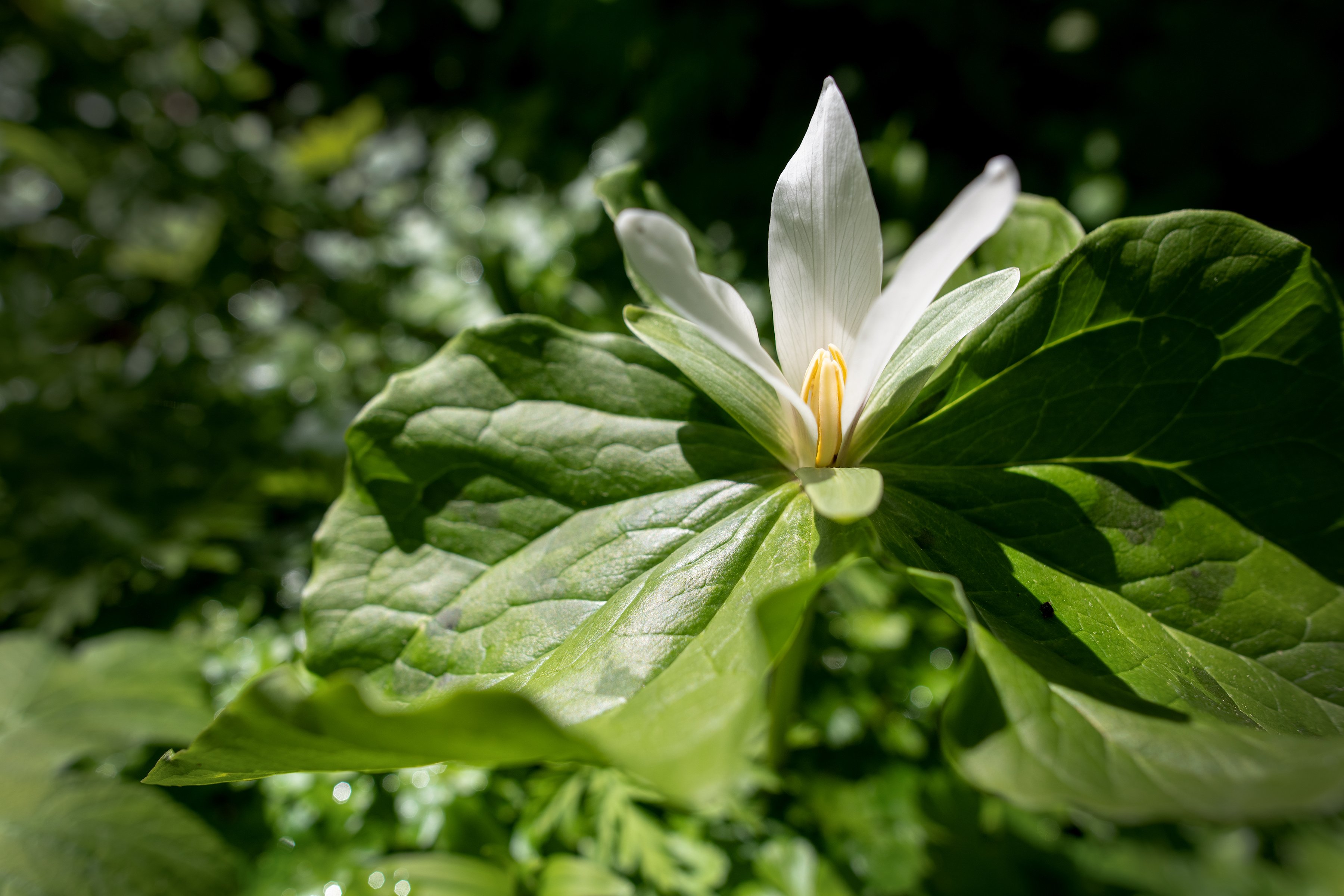
Mountain girl that I am, trillium is one of my favorite flowers. TechnicallyTrillium ovatum, also known as Pacific trillium, is what I think of when I think “trillium” because it’s the one I grew up with in the Coast Range of Oregon. Trillium plants look simple (just three petals and three sepals), but they are actually a complex little botanical. They live for decades, so you can form long-term relationships with them and welcome them back year after year. Unfortunately, however, they are slow to develop and spread, which is a serious weakness in the face of habitat loss and rampant wildharvesting. Between land use issues, trillium collectors who dig up wild varieties, deer who love to munch its leaves, and herbalists who seek out the rhizomes to make potent formulations, wild trillium is now in trouble. Let’s take a look at an age-old herbal ally and what we can do to preserve this beautiful, fragile plant.
The Botany Section: Why it’s Important to Leave Wild Trilliums Alone
According to the United States Department of Agriculture, there are 43 species of trillium around the world, 38 of which can be found in North America and five which are found in Asia. Trillium erectum is the species best known for its medicinal properties, but actually several trillium species contain the chemical compounds called sapogenins that have been utilized in herbal formulations for thousands of years as astringents, coagulants, expectorants, and stimulants for the uterus (which is how trillium got nicknames like “birth root”).
All trillium species belong to the Liliaceae (lily) family and are generally divided into two major groups: pedicellate trilliums (the flower sits on a small stalk that extends out from the plant) and sessile trilliums (the flower appears to rise directly from the bracts with no stalk). Both groups share some interesting complexities in propagation.
Trillium is very slow growing; it takes decades to establish a healthy, vibrant colony. If left undisturbed, it will ultimately spread by rhizomes to create a carpet of early-spring flowers on the forest floor. It can also propagate by seed, but this is even slower. Like many other spring ephemerals, it belongs to a group of plants that spread seed via ants (also mice). The seeds have a fatty white substance on them called elaisome, that ants love. The ants carry the seeds to their colony’s underground midden where they eat the elaisome but discard the seed itself. Those discarded seeds might germinate in the organically rich environment of the midden, but that takes two years because they have what is called a “double dormancy.” After one year underground, a root appears, followed by a little rhizome. The seedling then remains there for another year, at which point it will finally grow its first leaf (actually a bract that is leaf-like). Two more years will pass before the seedling produces the classic whorl of three leaves (bracts) that we are familiar with.
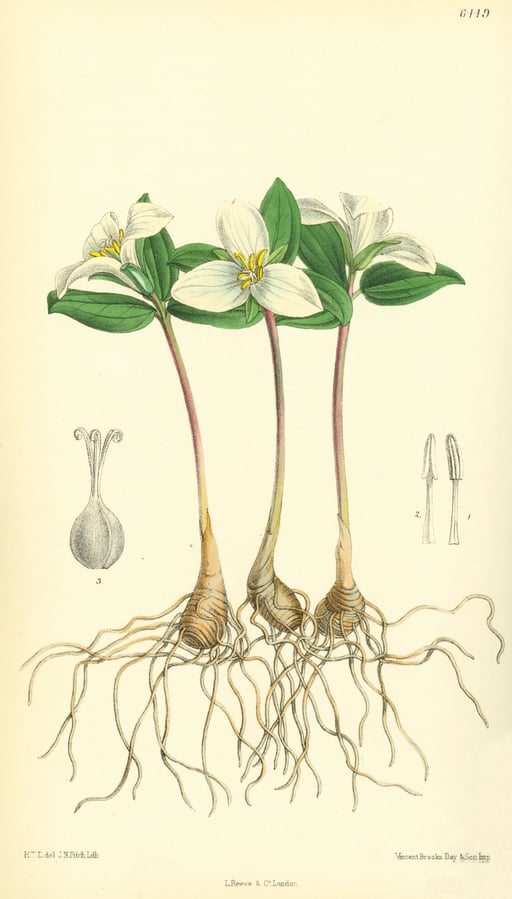
Photo From the Collection of The Lloyd Library and Museum.
It takes several more years for the trillium to store up enough energy to produce a flower. In an ideal situation, a single trillium may be seven or eight years old before it produces its first flower, and if conditions aren’t ideal, it can take a decade. Also, if the bulb is disturbed while in bloom (which sometimes happens when collectors set out to find trilliums to transplant), that plant may not bloom again for several more years. When you see a large population of flowering trillium, that colony could easily be 50 years old!
Although picking the flower does not harm the plant, it does keep it from making seeds that year, so picking flowers impacts the longterm health of the colony. Picking the green leaves can kill a trillium because, as with other bulbs, if you remove the leaves, the plant can’t make food. Since trillium only has three leaves to start with and because it generally lives in shaded woodlands, it needs all of its leaves for photosynthesis, in order to suck up every bit of spring sunlight and nutrients it can before the tree canopy leafs out above it. When a well-established trillium has leaf damage or loss, it might be able to recover by skipping flowering for a few years until it can rebuild its reserves. But younger plants with smaller rhizomes often don’t have the ability to survive the same kind of damage. It is easy to accidentally kill trillium through attempts to transplant from the wild or to harvest rhizomes.
Combine trillium’s slow propagation with other pressures like deer predation, an increase in invasive species, and loss of habitat due to changes in land use, and you start to see why trillium is in danger. Now add in the fact that trillium is one of the most frequently stolen plants in the wild! Because it takes so long to germinate and flower, it isn’t a profitable plant for most nurseries, which means there is a market for poached plants for both trillium collectors and wildharvesters who want the rhizomes to sell to herbal distributors or for personal formulations. A few people can decimate a healthy trillium colony in very little time and the colonies rarely recover. It is no wonder that everyone—from Mountain Rose Herbs, to United Plant Savers (UpS), to the U.S. Forest Service—begs people to purchase cultivated trillium plants from a reputable nursery rather than ever wildharvesting this precious plant.
Take Action to Help Trillium
- If you cannot find cultivated trillium, seek out alternative herbs. For instance, raspberry leaf and motherwort are excellent substitutes for trillium as an astringent, especially for the reproductive system. Speak with a qualified herbalist to determine which herbs might be good allies for you.
- Spread the word in your community and on trails. Help people learn not to pick or disturb trillium.
- Support local chapters of the Native Plant Society and/or UpS and learn more about your local ecosystem.
- Grow Your Own—Virtually all the trillium in the herbal supply chain is currently wildharvested in spite of the fact that it can be cultivated. Some nations are exploring cultivation; for instance, there are efforts in Pakistan to cultivate their native Trillium govanianum due to pressure from overharvesting. But these worthy efforts are obviously going to take time and patience. In the meantime, we can take pressure off of the wild population and enjoy these beautiful spring flowers by growing our own and by supporting ethical nurseries.
How to Grow Trillium
- Talk to your local native plant society and/or nurseries to find out if trillium can be grown in your region. Some varieties require very specific conditions—for instance, West Coast species prefer a mild maritime climate—but there are trilliums that can be grown from zones 3-9.
- Purchase trillium plants from a reputable local or online nursery. If you cannot find a local, reputable option, search online and be sure to ask where they source their native wildflowers. Ideally the plants will be several years old so they will be vigorous and will soon flower.
- Plant in full to partial shade. Remember, however, that early season sunlight is necessary for survival (before the trees leaf out above and take all the sunshine), so avoid planting in areas that get no sun in the early spring.
- Plant in rich soil with good drainage. Rhizomes can rot and plants can be troubled with fungal diseases in poorly drained soil.
- Avoid planting with highly competitive plants; trilliums are not an aggressive species and struggle to hold their own against feisty competitors.
- Mulch with leaves to replicate the forest floor trilliums call home.
- Water regularly during the growing season, until plant goes dormant.
- Trillium often dies back in the heat but don’t ever cut them back.
Interested in knowing what you can do for other at-risk herbs?
Read about Osha: Another Supportive, But At-Risk Plant Ally
You may also enjoy:
- 10 Underused Herbs for Wellness
- Organic Herb Sourcing: The Bigger Picture
- Stinging Nettle Identification, Benefits & Recipes













